Artificial Intelligence
AI Policing and Surveillance: How Technology Is Changing Law Enforcement
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the landscape of law enforcement and public safety. With innovations like drones, facial recognition, and real-time surveillance, AI is enhancing crime detection and prevention. However, as these technologies evolve, they bring forth pressing concerns about privacy and ethical implications. Explore how AI is transforming policing while navigating the delicate balance between innovation and civil liberties.

Have you asked yourself how artificial intelligence alters the face of safety and crime? The use of artificial intelligence in surveillance, monitoring and integration of data has brought new powerful tools for contemporary law enforcement and public safety.
What is surveillance policing?
From drones to real-time crime centers, the application of AI driven technology is unrivalled. But how does this translate to accuracy, efficiency, and privacy, in everyday business practice? Bear with me as I discuss these areas in an effort to demonstrate both the potential and the problems with using artificial intelligence in policing.
How Does AI Transform Real-Time Surveillance and Monitoring?
AI policing and surveillance in law enforcement can be smarter as well as wider. But what are the tools making this possible?
Surveillance and Predictive Policing through AI:
Cameras that have machine learning capabilities can watch for dozens of hours of video, note atypical actions, and identify abandoned packages. These are time saving and reduce human factors as much as possible.
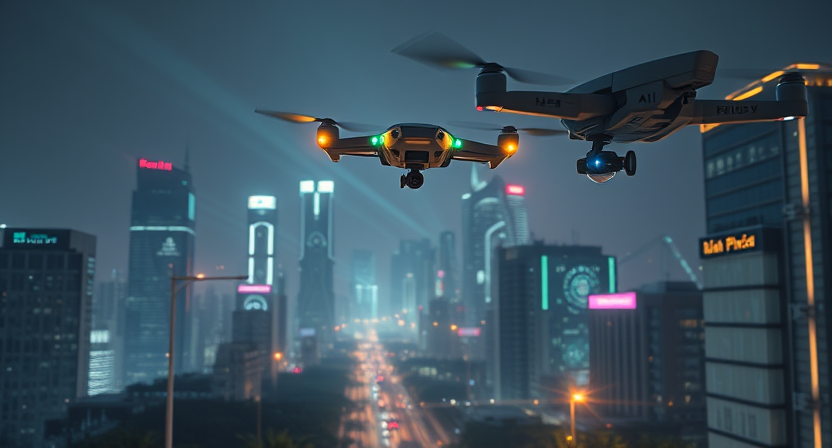
Role of Drones in Security:
The use of drone equipment with AI is useful in the fast scanning of an area when a physical presence is not feasible. They can easily provide coverage to large or areas that are hard to reach.
Internet of Things (IoT):
That is when IoT devices collect data from related systems, such as traffic cameras or smart city sensors, for straightforward integration to enhance situational awareness.
Predictive Analytics for Threat Detection:
Intelligence systems use the AI models to analyze big and current data for patterns that might indicate risks. This approach fits well in high risk scenarios and provides security teams with the power of pre-incident detection; a key advantage.
Facial Recognition Technology:
Facial identification technology entails the use of AI by matching faces to databases meaning identification and verification results are quickly produced. It improves security on who can access specific areas, follows the movement of suspects, and increases the effectiveness of security forces in crowded places while paying attention to privacy issues.
Automated Incident Response:
AI can be used in the development of systems that will respond to incidents automatically as they occur. Such systems can launch the lock down process, inform the authorities and the proper safety measures can be enforced without delay thus minimizing the amount of damage done.
AI-Powered Audio Analysis:
Real-time audio recognition translates sound patterns into potential danger level, including gunshots, alarms, or threats. This technology expands the typical security features since it turns to audio signals for detection of threats in loud or vast spaces.
Real-Time Data Processing:
The real-time data processing guarantee that vital information from many sources is analyzed immediately. The capability also fosters real-time analytics, which helps the security personnel to make faster decisions than otherwise in the event of an emergency.
Integration with Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing provides the capability to store and process the data required by sophisticated AI security applications. It provides access to the data, simplifies the procedure of updating and adaptation to organizations’ requirements, which makes it an integral part of modern security systems.
Behavioral Analytics:
Behavioral analytics entails monitoring of normal patterns of conduct with a view of identifying anomalies or suspicious conducts. With the help of getting to know typical patterns of behavior, AI is able to identify outliers, which is the basic principle of preventing insider threats and other dangerous scenarios.
AI becomes beneficial in these technologies as it increases the rate of threats identification. But fewer false alarms mention another benefit that is less noted.
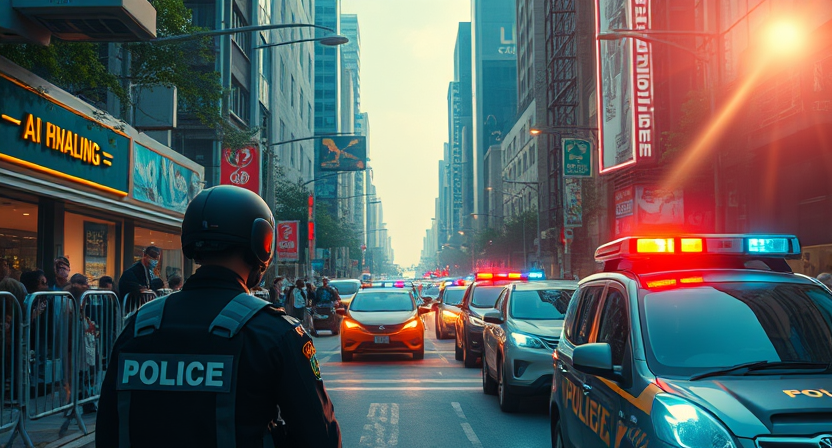

Why Are Bodycams Evolving With AI:
Bodycams make police work transparent, but watching the video footage is time-consuming. How is AI simplifying this?
Automatic Tagging with AI:
AI can tag people, places, and things if it is given a footage to go through. Facial recognition and other features are changing investigations as it is seen in the following ways.
Challenges in Deployment:
This makes it expensive, hence stifle common usage and; issues regarding ethical use present themselves with these solutions. That still does not eliminate their ability to provide fair analyses of incident occurrences.
AI-Assisted Real-Time Analysis:
The technology is already being utilized for real-time analysis of body-worn camera footage in order to give an officer an alert for something suspicious or risky. For example, AI may notice weapons or a rising tension in the frame, which would prevent the shoot out before it happens. This preventive measure reduces risk on the part of the officers and members of public at large.
Enhanced Evidence Review:
The second is an enhancement of reviewing evidence as one of AI’s most significant benefits. This means that when using AI, investigators will spend fewer hours watching hours of footage in order to find the relevant moments. Machine learning algorithms are able to extract particular events like certain contacts or shifts in position, which offers to an investigator concrete, useful data.
Data Storage Optimization:
Bodycams produce a lot of data, and this becomes a problem as regards storage and organization. AI policing and surveillance in law enforcement can improve the way that it stores data by tagging important clips while reducing the dimensions or bit rate of clips which are not as important. Further, AI tools can sort and store clip according to specific category for easy reference in case of legal matter or internal investigation.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Dilemmas:
As AI brings efficiency in the results, privacy issues still prevail to be a major concern. Some of the ways in which such technologies may violate people’s right or result in bias include: Other issues of ethical concern are on consent, the owners of the data, and concerns as to whether the collected data will be misused. This is the reason why police departments take time to balance between the advantages of implementation of technology in policing and the civil liberties.
Future of AI in Bodycams:
The possibilities of the AI in bodycams will remain so bright as the technology unceasingly advances. The current sophisticated algorithms may include features such as multilingual transcription, and even the ability to predict or recognize the emotions of a person further boosting the abilities of law enforcement. However, it will be important to have ethical deployment and public trust in order to determine how AI is going to be used in today’s policing.
Can AI Detect Threats Faster Than Humans?
In threat detection systems, AI can predict and maintain action before a crime occurs. How does this happen?
Suspicious Behavior Analytics:
Usually, AI algorithms study the behaviors of people and compare them with past behaviors in an area to identify any deviations, for example, moving around in restricted areas for several minutes.
Case Studies of AI in Action:
For instance, using AI in crowded events has halted armed attacks by identifying the incidents early in advance. These implementations are life and resource savers.
Predictive Threat Modeling:
AI is capable of predictive threat modeling where through analysis of past records of the organization’s activity AI can predict and prevent potential security threats. These systems can employ decision making algorithms to detect patterns that might not be immediately apparent to an operator and determine where and when threats might be likely to appear so that preventive steps can be taken. This approach turns security from being a reactive factor to being more proactive.
Real-Time Event Monitoring:
Monitoring and responding to events as they occur by the use of AI makes the process continuous with immediate action possible for any new threat. AI systems work in conjunction with live camera feeds, identify intruder or increasing violence, and inform security personnel at once. This can be used to quickly make decisions and also to counter threat before they become threats to the organization.
AI-Driven Risk Assessment:
Risk analysis by AI takes into account not only environmental factors, behaviour of people in certain places or during specific events, and known threat scenarios are assigned risk levels. These enables focus on resources and fortification of defense mechanisms by offering segmented analyses of risk hence reducing risks.
Crowd Behavior Analysis:
Crowd behavior analysis with the help of artificial intelligence implies patterns recognition of a crowd for search of signs of distress, panic or aggression. These systems are enabled by algorithms and can actually forecast crowd-related events, including stampedes or riots, based on fluctuations in movement or grouping. This helps to manage crisis and improve safety in areas with high population to some extent.
AI Integration with Existing Security Systems:
AI solutions can be integrated easily with existing security systems and this integration makes the solutions more effective and fast. For instance, AI can improve old trends of CCTV cameras by intelligent analysis or improve the access control systems to detect violations. This integration allows organisations to apply sophisticated AI capabilities to their existing structures and initiatives without requiring a significant reform.
Stories like these highlight how safety is in a position to leverage technology as a force multiplier without the constant supervisory influence.
What Role Do Real-Time Crime Centers Play?
Real-Time Crime Centers (RTCCs) are fast emerging as the central command of artificial intelligence policed societies. Let’s analyze why they are important now.
How Data Integration Works:
RTCCs take feeding data from other sources including surveillance cameras or perhaps public reports and feed it to officers with actionable insights in real time.
Benefits for First Responders:
AI in RTCCs means that agencies act quicker and more efficiently because the system is able to predict where an event may take place.
Centralized Data Analysis:
An aspect of the Real-Time Crime Center is the fact that there is a conglomeration of big data from a number of sources. If data from databases, sensors, and live feeds are combined, RTCCs dispose of the problems of isolated structures. This centralized approach helps the decision makers to be informed well also to discover the patterns, trends, and looming threats effortlessly.
AI-Enhanced Decision Making:
AI tools in RTCCs process the data received and even identify the material faster and more accurately than in traditional ways. In surveillance, artificial intelligence is used in flagging of any abnormalities in the footage, as well as in the classification of incidents according to their levels of severity. Through the exclusion of noise and providing substantial data to be used in decision making AI enables the law enforcement officers to make good choices when it comes to critical decision making.
Real-Time Collaboration Among Agencies:
They serve as an interface between the local police department, paramedics, firefighters, other agencies or even federal agencies during live coordination. The problem of working on the same database makes the communication between the teams faster and allows for synchronized actions during the mass-crisis situations. At this level of integration, there is a common response to high risk cases, which makes results much better.
Proactive Crime Prevention:
The preventative abilities of RTCCs are changing the nature of police work in a positive way. Using the approach of a predictive model, RTCCs can locate places with increased risk of crime or signs of new threats. Consequently, officers can be easily deployed before a crime occurs thus using the approaches that will change the policing strategies from reactive to tactical.
Improved Situational Awareness for Officers:
The use of maps and real time feeds, and of course the use of artificial intelligence allow officers to have an overall picture of events as they unfold. RTCCs provide textual descriptions, maps, and other updates that help to inform field teams as much as they want to know. It improves the security of the police officers and guarantees that the solutions are unique to each situation.
This characteristic of RTCCs explains the reason why they are essential to contemporary security networks.
How Can Privacy and Ethics Coexist With AI Policing?
That is where AI comes with a higher level of surveillance, which is an essential aspect, but it brings a raft of ethical concerns in regard to privacy. What should we concentrate on in order to bring the balance of these problems?
Key Legislation on Surveillance Use:
The governments are passing legislation to control use of AI to make sure that safety does not trump rights of the people. Thus, there are still weaknesses in the policies of nations around the world.
Solutions for Ensuring Ethical AI:
Public questioning, algorithm transparency, and message clarity comprise a structure that guarantees the AI instruments’ compliance with privacy restrictions while enhancing security.
Balancing Privacy and Security:
In this case, ensuring that the appropriate standards of privacy and security of the general public are met when deploying artificial intelligence in surveillance is crucial. Excessive concentration on security often results in the violation of people’s privacy with such practices as a form of spying getting endorsed, compromising civil liberties. However, failing to estimate security needs could have undesirable consequences and place the communities at risk. There is a need to develop strong measures for introducing better accountability and to ensure that privacy becomes a principle in developing and implementing AI systems. The public also needs to be informed on how data is gathered, processed and used in an effort to realize this balance.
Ethical Guidelines for AI in Policing:
Policing with the help of AI has some ethical concerns as its effective implementation is a matter of concern. This helps in avoiding unjustified use of the tools in a way that renews biases and promotes unjustified surveillance. Transparency is central; law enforcement agencies should run their AI systems according to processes that are clearly spelled out in accordance with human rights laws. Some suggestions include the establishment of ethical oversight boards whose duty would be to assess whether or not certain AI technologies can be used in policing and other similar scenarios, and address the issue of misuse.
Importance of Accountability in AI:
As it has been highlighted, accountability in AI surveillance systems means that mistakes or even prejudice or misuse are quickly detected and corrected. The entities using AI for public safety must be in a position to justify their decisions and fully own the consequences derived from such decisions. Global best practices for building misuse case databases should include open reporting hotlines for misuse cases and promote independent audits of social context of such tools.
Public Trust and Transparency:
To build public trust in AI technology, there must be the disclosure of the AI technology used. In other words, people have to know how surveillance systems work, what information is being gathered and for what purpose. Prominently sharing information on protection and constraints alongside guaranteeing that reusable code is open to the public and frequently discussed can make cooperation between governments, developers, and citizens more trustworthy. Information sharing also promotes the consideration of all the stakeholders in policy making formulations to enhance the creation of transparency.
Global Standards for AI Surveillance:
One limitation of AI surveillance to ethical use is the continued absence of guidelines on how this technology should be implemented across countries. Analysis of the potential risks demonstrates that a coordinated framework incorporating the principles of universal human rights could act as a starting point for minimizing the risks and establishing a basic framework for the correct use of tools. It is suggested that nations should work together to design compatible standards which are fair, secure and ethical appropriate for cultural and legal differences. International involvement in regulatory proceedings can also promote the development of this common outlook in an effort to achieve homogeneity of regulation.
In your opinion is current regulation sufficient in protecting individual rights in relation to using AI? This is a massive issue for legislators and for us as voters.
Conclusion:
AI is the key that will transform the perception of policing from the perspective of prevention of crimes to policing and community interactions.
We’ve looked at what it can and cannot do, as well as what is right and wrong to do with it. Criticisms of AI is that while it gives a chance of productive AND safe improvement, its future is tied with the use of the responsible methods for human rights.
Should we rely more on AI-driven systems, or does this move us closer to a surveillance state? Share your thoughts and concerns – your voice matters.
-

 Artificial Intelligence8 months ago
Artificial Intelligence8 months agoWhat is Artificial Intelligence? A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses and Enthusiasts
-

 Artificial Intelligence6 months ago
Artificial Intelligence6 months agoHow to Use Grok AI: A Complete Guide
-

 Artificial Intelligence8 months ago
Artificial Intelligence8 months agoUnlocking the Power of Artificial Intelligence Tools
-

 Artificial Intelligence7 months ago
Artificial Intelligence7 months agoWhat is DeepSeek? Revolutionizing AI with Cutting-Edge Solutions
-

 Artificial Intelligence3 months ago
Artificial Intelligence3 months agoAI Technologies in Warehouse Automation:
-

 Artificial Intelligence4 months ago
Artificial Intelligence4 months agoMeta’s AI Push: The Standalone Assistant App Set to Rival ChatGPT
-

 Artificial Intelligence3 months ago
Artificial Intelligence3 months agoHow Artificial Intelligence is Revolutionizing Logistics:
-

 Artificial Intelligence3 months ago
Artificial Intelligence3 months agoPredictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting: